pg_cron
1. Overview
Running periodic tasks in PostgreSQL, such as executing VACUUM or deleting old data, is a common requirement. A simple way to achieve this is to configure cron or other external daemons to periodically connect to the database and run commands. However, as databases increasingly run as managed services or standalone containers, configuring and running a separate daemon often becomes impractical. Additionally, it’s difficult to make your cron jobs aware of failover or schedule tasks across cluster nodes.
pg_cron is an open-source scheduled task extension for PostgreSQL that allows setting up cron-style task scheduling directly within the database for automating data maintenance tasks (cleanup, aggregation), database health checks, executing stored procedures and custom functions, and other operations. It stores cron jobs in tables, and periodic tasks automatically fail over with the PostgreSQL server. For more details, see pg_cron documentation.
2. Installation and Configuration
| The source installation environment is Ubuntu 24.04 (x86_64). IvorySQL 5 or higher version is already installed in the environment, with the installation path at /usr/local/ivorysql/ivorysql-5 |
2.1. Source Installation
# Clone pg_cron source code git clone https://github.com/citusdata/pg_cron.git cd pg_cron # Set pg_config path to PATH environment variable, e.g.: export PATH=/usr/local/ivorysql/ivorysql-5/bin/:$PATH make make install
2.2. Configuration File (ivorysql.conf)
# Shared preload extensions shared_preload_libraries = 'pg_cron' # Specify task metadata storage database (default current database) cron.database_name = 'ivorysql' # Maximum number of concurrent tasks allowed cron.max_running_jobs = 5
2.4. Create Extension and Confirm pg_cron Version
Connect to the database with psql and execute the following commands:
ivorysql=# CREATE extension pg_cron; CREATE EXTENSION ivorysql=# SELECT * FROM pg_available_extensions WHERE name = 'pg_cron'; name | default_version | installed_version | comment ---------+-----------------+-------------------+--------------------------- pg_cron | 1.6 | |Job scheduler for PostgreSQL (1 row)
3. Core Functionality Usage
3.1. Creating Scheduled Tasks
SELECT cron.schedule(
'nightly-data-cleanup', -- Task name (unique identifier)
'0 3 * * *', -- Cron expression (daily at UTC 3:00)
$$DELETE FROM logs
WHERE created_at < now() - interval '30 days'$$ -- SQL to execute
);
Cron expression quick reference:
Example |
Meaning |
'0 * * * *' |
Execute every hour on the hour |
'*/15 * * * *' |
Execute every 15 minutes |
'0 9 * * 1-5' |
Execute at 9 AM on weekdays |
'0 1 1 * *' |
Execute at 1 AM on the 1st of every month |
pg_cron also allows using '$' to represent the last day of the month.
3.2. Task Management
# View all tasks SELECT * FROM cron.job;
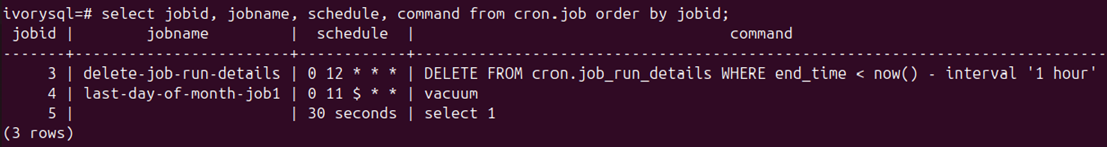
# View task execution history SELECT * FROM cron.job_run_details ORDER BY start_time DESC LIMIT 10;
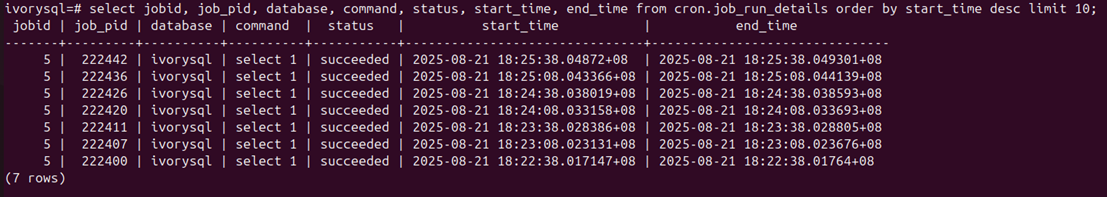
# Delete task
SELECT cron.unschedule('nightly-data-cleanup');
# Pause task (update status)
UPDATE cron.job SET active = false WHERE jobname = 'delete-job-run-details';